Are you looking to enhance your understanding of the essential concepts that are of utmost significance? In this article, we delve into a variety of topics and provide you with a wealth of knowledge that is bound to broaden your horizons. From uncovering the intricacies of these subjects to unraveling their profound implications, we leave no stone unturned in our quest to equip you with a holistic understanding.
Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey as we delve into a myriad of intriguing subjects that are often shrouded in mystery. Through meticulous research and thoughtful analysis, we aim to convey complex ideas in a manner that is both comprehensible and engaging. No matter your level of familiarity, be prepared to uncover fresh perspectives and thought-provoking insights that will leave you craving for more.
Our mission is to facilitate your learning experience and empower you with the tools necessary to navigate through the intricacies of these captivating subjects. By leveraging our expertise and passion, we aim to distill vast amounts of information into digestible portions, leveraging the power of clarity to ensure that you absorb each concept effortlessly. Along the way, we emphasize the significance of critical thinking and encourage you to challenge existing notions, empowering you to become an active participant in the exchange of ideas.
Understanding the Key Facts About Vaccinations
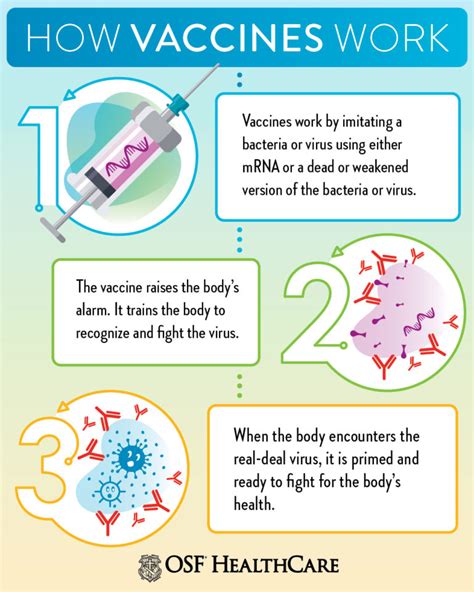
Delving into the realm of immunizations can provide a comprehensive understanding of their noteworthy significance in safeguarding public health. By exploring the vital aspects associated with the administration of vaccines, this section aims to shed light on their remarkable efficacy in preventing and controlling the spread of infectious diseases.
Unveiling the underlying principles, this segment offers insights into the fundamental working mechanisms of vaccinations. It focuses on deciphering how vaccines prompt the body's immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens, fortifying it against future encounters. Additionally, the section explores the remarkable role of herd immunity, elucidating how collective immunization can shield vulnerable populations.
Highlighting the diverse types of vaccines available, this section provides a comprehensive overview of the varied formulations. From live attenuated vaccines to subunit, conjugate, and mRNA vaccines, each type offers a unique approach to immunization. By understanding the key characteristics and benefits of different vaccine formulations, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their health.
Delving into the safety aspect of vaccinations, this section addresses common concerns and misconceptions. By examining rigorous regulatory processes and extensive monitoring systems, it establishes a foundation of confidence in the safety of vaccines. It emphasizes that the benefits of immunizations outweigh the potential risks, debunking prevailing myths and misconceptions.
Finally, this section explores the global impact of vaccines, emphasizing their role in preventing pandemics and saving countless lives. By providing real-world examples of diseases eradicated or significantly controlled through vaccination campaigns, it showcases the power and effectiveness of immunizations in shaping the course of public health.
| Key Takeaways: |
| - Fundamental principles of immunization |
| - Various types of vaccines and their benefits |
| - Addressing concerns and misconceptions about vaccine safety |
| - Global impact and success stories of vaccinations |
The Significance of Vaccination
Vaccination plays a vital role in safeguarding public health and preventing the spread of infectious diseases. It is an integral component of preventive medicine, focusing on the administration of vaccines to stimulate the immune system and build immunity against specific pathogens.
When individuals receive vaccines, it triggers their immune response, enabling their bodies to recognize and combat harmful microorganisms. Vaccination offers protection not only to the individuals receiving the vaccines but also to the wider community by reducing the risk of outbreaks and minimizing the transmission of diseases.
Vaccines have been instrumental in controlling and eradicating numerous diseases throughout history. From smallpox to polio, vaccines have helped to eliminate or significantly reduce the incidence of life-threatening illnesses. They have played a key role in saving countless lives and improving overall public health.
Additionally, vaccination contributes to the concept of herd immunity. When a large portion of a population is vaccinated against a particular disease, it creates a protective shield, making it difficult for the disease to spread and infect vulnerable individuals who are unable to receive vaccines due to medical reasons or age restrictions.
- Vaccines are extensively tested for safety and efficacy before they are approved for use. Rigorous scientific research and clinical trials ensure that vaccines are both beneficial and have minimal risks.
- Vaccination is particularly crucial for infants, young children, and individuals with weakened immune systems. By immunizing these vulnerable populations, we can safeguard their health and reduce the likelihood of severe complications or even death caused by vaccine-preventable diseases.
- The importance of vaccination extends beyond individual health. By choosing to get vaccinated, we actively participate in the collective effort to protect our communities, prevent the resurgence of diseases, and promote public health as a whole.
In conclusion, the significance of vaccination cannot be overstated. It is a vital tool in the prevention and control of infectious diseases, contributing to improved health outcomes for individuals and societies at large. By understanding the importance of vaccination and making informed choices, we can actively contribute to a healthier and safer future for everyone.
Understanding the Mechanics of Vaccination
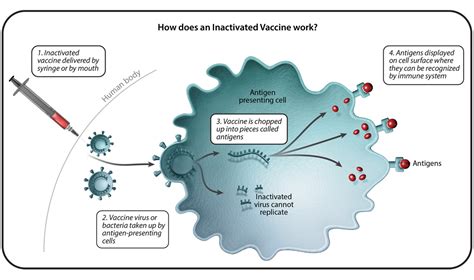
Vaccines play a pivotal role in safeguarding public health by offering protection against infectious diseases. This section will delve into the intricate workings of vaccines, unraveling the fascinating mechanisms that make them an effective defense against pathogens.
| Vaccine Types | How They Work |
|---|---|
| Inactivated Vaccines | These vaccines utilize pathogens that have been killed or inactivated to induce an immune response in the body. They stimulate the production of antibodies, ensuring protection when the person is exposed to the live pathogen in the future. |
| Live Attenuated Vaccines | Live vaccines contain weakened forms of the pathogen, enabling them to replicate and cause a mild infection in the body. This mild infection prompts the immune system to develop a long-lasting immune response, thereby conferring immunity to the person. |
| Subunit, Recombinant, or Conjugate Vaccines | These vaccines utilize specific parts of the pathogen, such as proteins or polysaccharides, to trigger an immune response. By presenting these antigens to the immune system, they train it to recognize and mount an attack against the actual pathogen. |
| Viral Vector Vaccines | These vaccines employ harmless viruses as carriers to deliver genetic material from the target pathogen into the body's cells. This genetic material then instructs the cells to produce viral proteins, stimulating an immune response and offering protection against the target pathogen. |
| Nucleic Acid Vaccines | These cutting-edge vaccines utilize genetic material, either DNA or RNA, to provide instructions to the body's cells on how to produce the target pathogen's proteins. This prompts the immune system to mount a defense, creating immunity against the pathogen. |
By understanding the different types of vaccines and their functioning, it becomes clear how these medical tools stimulate the body's immune system to recognize and combat infectious agents. This knowledge will enable individuals to make informed decisions regarding their own vaccination and contribute to the overall health of society.
Common Misunderstandings about Vaccines
There are a number of misconceptions surrounding vaccines that can cause confusion and misunderstanding. In this section, we will unravel some of these myths and provide accurate information to help you better understand the importance of vaccination.
One misconception is that vaccines cause the diseases they are designed to prevent. However, this is not true. Vaccines are carefully developed and rigorously tested to ensure their safety and effectiveness. They contain harmless versions of the virus or bacteria they protect against, which trigger the immune system to develop a defense without causing the actual disease.
Another common misconception is that vaccines can overload the immune system. This is not the case. The immune system is capable of responding to numerous antigens at once, and the number of antigens in vaccines is significantly lower than what the body encounters on a daily basis. Vaccines stimulate the immune system to produce a targeted response, strengthening its ability to fight off specific infections.
Some individuals believe that natural immunity acquired through infection is superior to vaccine-induced immunity. However, relying on natural infection for immunity can pose serious risks. Vaccines provide a safer alternative by simulating an immune response without the potential complications and dangers associated with the actual disease.
There is also a misconception that vaccines are unnecessary for certain diseases that are no longer prevalent. This notion can be dangerous, as it underestimates the potential for diseases to resurge if vaccination rates drop. Vaccination programs play a crucial role in preventing outbreaks and protecting individuals, as well as the broader population, from infectious diseases.
Lastly, a frequently misunderstood concept is that vaccines can cause autism. Extensive research has been conducted to investigate this claim, and there is no credible scientific evidence linking vaccines to autism. Vaccines are a crucial tool in protecting public health, and it is important to rely on accurate information when making decisions about vaccination.
| Misconception | Fact |
|---|---|
| Vaccines cause the diseases they are designed to prevent. | Vaccines contain harmless versions of the virus or bacteria they protect against. |
| Vaccines can overload the immune system. | The immune system is capable of responding to numerous antigens, and vaccines contain a lower number of antigens than the body encounters daily. |
| Natural immunity acquired through infection is superior to vaccine-induced immunity. | Vaccines provide a safer alternative to acquiring immunity without the risks associated with the actual disease. |
| Vaccines are unnecessary for diseases no longer prevalent. | Dropping vaccination rates can lead to disease resurgences, making vaccines vital for prevention. |
| Vaccines can cause autism. | No credible scientific evidence supports the claim that vaccines cause autism. |
Vaccines and Collective Protection

Understanding the significance of vaccines in achieving collective immunity is essential for comprehending the wider impact of immunization efforts. In this section, we explore the intricate relationship between vaccines and the concept of herd immunity, shedding light on its role in safeguarding communities against infectious diseases.
Immunization is not solely a means of safeguarding an individual's health, but also an effective strategy to protect the collective well-being of a community. Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight specific disease-causing agents, providing individuals with immunity against future infections. However, their impact extends far beyond the individual. When a significant portion of a population is immune to a particular disease through vaccination, it creates a barrier that prevents the disease from spreading effectively. This phenomenon, known as herd immunity, plays a vital role in protecting vulnerable members of society who may not be able to receive vaccines due to age, medical reasons, or limited access to healthcare.
By achieving high vaccination rates, communities can take advantage of the collective defense mechanism provided by herd immunity. This helps break the chain of disease transmission, reducing the overall burden of infectious diseases and minimizing the risk of outbreaks. Vaccines not only protect those who receive them but also indirectly shield those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Through vaccination, communities become resilient and united in their efforts to combat the spread of infectious diseases.
However, it is important to note that achieving herd immunity is a collective responsibility. High vaccine coverage rates are crucial to prevent the resurgence of diseases that can easily take hold if protection levels decline. Engaging in open and informed discussions about vaccines, addressing concerns, and promoting access to immunization services are integral to ensuring a society's collective protection. By staying informed and actively participating in vaccination programs, individuals contribute to the broader goal of creating healthier and more resilient communities.
Vaccination and the Future of Public Health
In this section, we explore the profound impact of vaccines on the well-being of society and the potential they hold for the future of public health.
Vaccination plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public health, protecting individuals, and preventing the spread of infectious diseases. By stimulating the immune system to produce an immune response, vaccines help the body recognize and combat harmful pathogens. As a result, they significantly reduce the occurrence and severity of infectious diseases and save countless lives.
Looking towards the horizon, the future of public health holds immense possibilities with advancements in vaccine technology. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to improve vaccine efficacy, durability, and accessibility. Novel vaccine platforms, such as mRNA vaccines, demonstrate promising results in both preventing and treating various diseases. These innovative approaches have the potential to revolutionize public health strategies and enhance disease prevention efforts globally.
Furthermore, vaccines are not limited to infectious diseases alone. Scientific advancements pave the way for vaccine development in areas such as cancer prevention and treatment, allergies, autoimmune disorders, and more. These breakthroughs have the potential to reshape the healthcare landscape, offering new avenues for disease prevention and management.
However, the future of vaccination also comes with challenges that need to be addressed. Ensuring vaccine education, trust, and accessibility are crucial for successful implementation and maximum societal impact. Public health initiatives must focus on dispelling misinformation, building confidence in vaccines, and addressing disparities to ensure that the benefits of vaccination reach all communities.
In summary, vaccines have been and will continue to be instrumental in shaping the future of public health. Their ability to prevent infectious diseases, advancements in vaccine technology, and potential applications beyond traditional vaccines open up incredible opportunities for disease prevention, management, and overall well-being of society.
FAQ
What is "All You Need to Know" about?
"All You Need to Know" is a comprehensive guide that aims to provide readers with all the necessary information on a specific topic.
Why should I read "All You Need to Know"?
Reading "All You Need to Know" is beneficial because it offers a concise and detailed explanation of the topic, saving you time and effort in conducting extensive research.
How can "All You Need to Know" help me in my daily life?
"All You Need to Know" can be helpful in your daily life by providing you with valuable insights, practical tips, and knowledge that can enhance your understanding and decision-making in various aspects related to the topic.
Where can I find "All You Need to Know" articles?
"All You Need to Know" articles can be found on reputable websites, blogs, and publications that specialize in the topic. They are often easily accessible and can be searched using specific keywords related to the subject matter.



