Replenishing our minds and bodies through a state of profound rest is an integral aspect of fostering optimal mental and physical well-being. Sleep, a fundamental biological function, plays a crucial part in maintaining our cognitive functions, emotional balance, and overall vitality. It is during these tranquil slumbers that our brains undergo essential processes of consolidation, organization, and rejuvenation - allowing us to awaken refreshed, rejuvenated, and ready to tackle the challenges of the day.
Recharging our cognitive batteries during sleep is not merely a passive state of unconsciousness but a dynamic and intricate dance that involves various stages and patterns of brain activity. From the initial stages of lighter sleep, characterized by rapid eye movement (REM), to the deeper stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, our brains perform a symphony of activities, including memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and neural connectivity refinement.
Fortifying our mental faculties through deep slumber helps us solidify the knowledge and skills acquired during our waking hours. It is during REM sleep that our brains actively process and integrate new information, establishing connections and associations that aid in long-term memory formation. This consolidation process not only enhances our ability to retain facts and figures but also enables creative problem-solving, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence.
Moreover, sleep is not solely concerned with bolstering our cognitive capabilities; it serves as a key component in rejuvenating our physical health as well. The hours we spend in deep repose are fundamentally linked to our body's restorative processes, such as tissue repair, hormone regulation, and immune system function. During slumber, our bodies produce crucial hormones, including growth hormone, that aids in muscle repair and recovery, while the immune system works diligently to strengthen its defenses against viral and bacterial invaders.
The Significance of Rest for Cognitive and Physical Well-being

Adequate sleep plays a pivotal role in supporting optimal mental and physical health. A crucial element of maintaining overall well-being, slumber not only rejuvenates the mind and body but also facilitates important processes essential for cognitive functioning and physical vitality. Sleep's profound influence extends beyond mere rest and recovery, encompassing various aspects of our lives, including mood, memory, immune system function, and even productivity.
- Enhances Brain Function: Quality sleep fosters improved cognitive abilities, such as concentration, problem-solving skills, and creativity. It promotes optimal brain function, enabling individuals to better retain information, make sound decisions, and think critically. Conversely, inadequate sleep can impede cognitive performance, leading to decreased focus, diminished memory recall, and impaired judgment.
- Boosts Emotional Well-being: Sufficient sleep is essential for emotional stability and resilience. It helps regulate mood by facilitating the processing of emotions and enhances the ability to manage stress effectively. Restful slumber improves overall emotional well-being, while sleep deficiency is associated with heightened irritability, mood swings, and an increased risk of developing mental health disorders.
- Strengthens Physical Health: Restorative sleep contributes to a robust immune system, reducing the likelihood of illness and promoting overall physical health. During sleep, the body repairs damaged tissues, releases growth hormones, and regulates metabolic processes critical for maintaining an optimal weight. In contrast, chronic sleep deprivation can weaken the immune system, increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, compromise hormone regulation, and negatively impact overall physical performance.
- Improves Energy and Vitality: Quality sleep is vital for replenishing energy stores and promoting sustained vitality throughout the day. Adequate rest enhances physical stamina, enabling individuals to engage in regular exercise and perform daily tasks with greater efficiency. Inadequate sleep, on the other hand, often leads to feelings of fatigue, decreased motivation, and reduced productivity, hindering overall physical and mental performance.
In conclusion, recognizing the significance of sleep for both mental and physical well-being is essential. Prioritizing sufficient and restful slumber enables individuals to optimize cognitive function, nurture emotional health, strengthen physical resilience, and enhance overall vitality. By embracing the value of sleep, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving and maintaining holistic well-being.
Sleep and Brain Function: The Critical Connection
Understanding the essential link between sleep and brain function is of utmost importance when considering our overall well-being. It is no secret that quality rest plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal mental and physical health. However, the intricate relationship between sleep and the brain goes far beyond simply feeling energized and refreshed upon waking. Exploring the critical connection between these two factors reveals a fascinating and complex interplay that extends to various aspects of cognitive function, emotional regulation, memory consolidation, and overall brain health.
Exploring Cognitive Function:
Quality sleep acts as a foundation for cognitive processes, encompassing attention, concentration, problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity. Regular and sufficient sleep is vital for maintaining mental clarity, enhancing cognitive flexibility, and fostering effective information processing. Without ample sleep, individuals may experience difficulties in these areas, leading to decreased productivity, impaired focus, and inefficiency in daily activities.
Influence on Emotional Well-being:
Sound sleep is known to regulate emotional well-being, aiding in emotional resilience and stability. Sufficient rest allows the brain to effectively process and regulate emotions, contributing to improved mood, decreased stress levels, and overall psychological well-being. On the contrary, inadequate sleep can disrupt emotional regulation, increasing vulnerability to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and even depression.
The Role in Memory Consolidation:
Sleep plays a critical role in memory consolidation, the process by which memories are strengthened and stored for long-term retention. During sleep, the brain actively processes and enhances the memories from the events and experiences of the day. This consolidation process is essential for learning, as it helps solidify newly acquired information and skills into the neural connections of the brain, improving recall and overall cognitive performance.
Promoting Brain Health:
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining optimal brain health and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. During sleep, the brain undergoes necessary processes that eliminate waste products, restore cellular energy, and repair damaged neurons. Chronic sleep deprivation disrupts these vital functions, potentially leading to cognitive decline, increased risk of developing conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, and other neurological disorders.
The Interplay of Sleep and Brain Function:
The relationship between sleep and brain function is bidirectional and highly interconnected. While quality sleep supports optimal brain performance, the brain itself regulates the sleep-wake cycle and influences the quality and duration of sleep. Therefore, prioritizing and prioritizing sleep habits and implementing healthy sleep hygiene practices are crucial for maintaining a thriving and well-functioning brain.
In conclusion, recognizing the critical connection between sleep and brain function provides insight into the profound impact that sufficient and restorative rest can have on our mental and physical well-being. By understanding the broader implications and interdependencies, we can emphasize the importance of prioritizing and nurturing healthy sleep habits to optimize cognition, emotional resilience, memory consolidation, and overall brain health.
Sleep Deprivation and its Impact on Cognitive Abilities

Understanding the influence of sleep deprivation on cognitive abilities is crucial in comprehending the significance of adequate sleep for optimal mental and physical functioning. The absence or insufficient amount of sleep can have detrimental effects on various cognitive processes and impair vital aspects of human cognition.
Effects on Decision-Making and Problem-Solving: Sleep deprivation can significantly hinder one's ability to make sound decisions and solve complex problems. Lack of sleep compromises cognitive flexibility, reasoning skills, and logical thinking, making it challenging to assess situations accurately and come up with effective solutions.
Impaired Attention and Concentration: Inadequate sleep adversely affects attentional processes, resulting in decreased focus, reduced concentration span, and difficulty in sustaining attention. This can lead to decreased productivity, impaired learning capabilities, and increased susceptibility to distractions, ultimately impacting overall cognitive performance.
Memory Consolidation and Learning: Sleep plays a vital role in memory consolidation, a process crucial for effective learning and retention of information. Insufficient sleep disrupts this process, making it more challenging to acquire new knowledge, consolidate memories, and retrieve information accurately. Consequently, sleep-deprived individuals may experience difficulties in learning and retaining new concepts.
Emotional Regulation and Mood: Sleep deprivation can have a profound impact on emotional regulation and mood stability. Lack of sleep often leads to heightened emotional reactivity, increased irritability, and a greater susceptibility to negative emotions. This can impair decision-making abilities and negatively impact interpersonal relationships.
Slowed Reaction Time and Impaired Motor Skills: Sleep deprivation compromises motor skills, coordination, and reaction time, which are essential for performing various tasks safely and efficiently. Impaired motor skills increase the risk of accidents and injuries and can negatively affect everyday activities requiring precise movements and quick reflexes.
Overall Cognitive Decline: Prolonged sleep deprivation can lead to a decline in overall cognitive functioning. Continuous insufficient sleep can contribute to long-term cognitive decline, including difficulties in attention, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making, ultimately affecting one's mental well-being and overall quality of life.
In conclusion, recognizing the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive abilities emphasizes the importance of prioritizing sufficient sleep for maintaining optimal mental and physical functioning. Adequate sleep is essential for cognitive processes such as decision-making, attention, memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and motor skills, all of which significantly contribute to an individual's overall well-being.
The Impact of Sleep on Emotional Regulation and Mental Health
Sleep plays a crucial role in the regulation of emotions and the maintenance of mental well-being. Adequate sleep is essential for optimal emotional functioning, as it allows the brain to process and regulate emotions effectively. Without sufficient sleep, individuals may experience difficulties in managing their emotions, leading to detrimental effects on their mental health.
Quality sleep facilitates the consolidation of emotional memories and helps regulate emotional responses. During sleep, the brain processes and integrates emotional experiences, enabling individuals to cope with daily stressors and emotional challenges. This consolidation process enhances emotional resilience and allows for adaptive emotional regulation in various situations.
Furthermore, sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of hormones and neurotransmitters that are crucial for emotional stability. Inadequate sleep has been associated with increased levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can intensify emotional reactivity and impair cognitive functioning. Additionally, sleep deficiency can affect the production and regulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play vital roles in mood regulation and emotional well-being.
Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep duration have been linked to various mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression. Individuals who consistently experience disturbed sleep patterns are more likely to exhibit symptoms of these conditions. Furthermore, the bidirectional relationship between sleep and mental health suggests that untreated mental health disorders can also contribute to sleep disturbances, creating a cycle that further affects emotional regulation.
In conclusion, sleep plays a fundamental role in emotional regulation and mental health. A lack of adequate and restful sleep can disrupt the brain's ability to process emotions effectively, leading to difficulties in regulating emotions and potentially contributing to mental health disorders. Prioritizing quality sleep is essential for maintaining emotional well-being and overall mental health.
Sleep and Physical Health: The Restorative Power
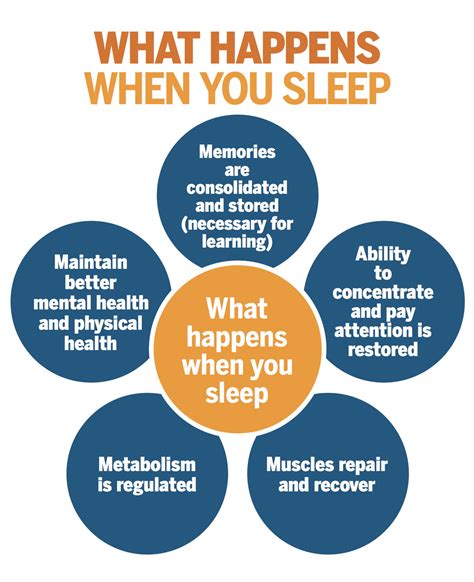
Sleep plays a crucial role in the overall well-being and maintenance of our physical health. It serves as a revitalizing mechanism that allows our body to recover, repair, and replenish its vital functions. The restorative power of sleep cannot be underestimated, as it affects various aspects of our physical health, including immune function, cardiovascular health, and hormone regulation.
| Immune Function: | Sleep enhances the immune system's ability to defend the body against harmful pathogens, viruses, and diseases. It promotes the production of cytokines, which are essential in fighting infections and inflammation. |
| Cardiovascular Health: | Adequate sleep contributes to a healthy heart and blood vessels. It helps regulate blood pressure, reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease and stroke, and supports the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system. |
| Hormone Regulation: | Sleep plays a vital role in regulating hormone levels in the body. It helps maintain a balance of hormones that control appetite, metabolism, growth, and development. Sufficient sleep is crucial for optimal hormonal function. |
In addition to these key aspects, quality sleep also promotes muscle recovery, enhances physical performance, and aids in weight management. It is during deep sleep that the body repairs and rebuilds tissues, strengthens muscles, and consolidates memory. By prioritizing and ensuring adequate sleep, individuals can experience the full benefits of physical health and well-being.
How Lack of Sleep Impacts the Immune System
Insufficient sleep has significant consequences on our body's defense mechanism, known as the immune system. When we do not get enough sleep, our ability to fight off infections and illnesses becomes compromised, leaving us more vulnerable to a range of health conditions. The interplay between inadequate sleep and the immune system is a complex relationship that warrants further exploration.
1. Increased susceptibility to infections: Lack of sleep weakens the immune system, making us more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections. This can lead to frequent colds, flu, and other respiratory illnesses. Moreover, the severity of these infections may also be heightened due to the compromised immune response.
2. Impaired immune response: Sleep deprivation affects the function of immune cells, including T cells, natural killer cells, and macrophages. These cells play a crucial role in identifying and eliminating foreign pathogens in our bodies. When we lack sleep, the production and activity of these immune cells are reduced, negatively impacting our ability to mount a proper immune response.
3. Inflammation and chronic diseases: Chronic lack of sleep can lead to a state of chronic low-grade inflammation in the body. This inflammatory response is associated with an increased risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders. Inadequate sleep also disrupts the balance of hormones involved in regulating inflammation, further contributing to the development of these conditions.
4. Delayed wound healing: Sleep deprivation can impair the body's ability to heal wounds effectively. During sleep, the body releases growth factors and hormones that promote tissue repair and regeneration. When we don't get enough sleep, this process is disrupted, leading to delayed wound healing and potential complications.
5. Altered vaccine response: Lack of sleep can affect the efficacy of vaccines. Studies have shown that individuals who do not get enough sleep may have a reduced immune response to vaccines, making them less protected against certain diseases. This highlights the importance of adequate sleep in maximizing the effectiveness of immunizations.
In conclusion, the impact of insufficient sleep on the immune system is undeniable. From impaired immune response to increased susceptibility to infections and chronic diseases, sleep deprivation has far-reaching consequences for our overall well-being. Prioritizing quality and quantity of sleep is crucial in maintaining a robust immune system and safeguarding our health.
Sleep and Weight Management: Surprising Interactions

Sleep plays a pivotal role in our overall well-being, impacting not only our mental and physical health but also unexpected areas such as weight management. The relationship between sleep and weight is a complex one, with various surprising interactions that warrant exploration.
1. Sleep Duration and Appetite Regulation
Studies have consistently shown that inadequate sleep duration can disrupt the hormonal balance responsible for regulating appetite. When we don't get enough sleep, our bodies produce higher levels of ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates hunger, while reducing levels of leptin, a hormone that signals fullness. Consequently, sleep deprivation can lead to increased food cravings and a tendency to overeat, often resulting in weight gain.
2. Sleep Quality and Food Choices
Quality sleep is not solely determined by the number of hours we spend in bed but also by the depth and restfulness of our sleep. Poor sleep quality has been linked to a higher preference for foods that are high in sugar, fat, and calories. Moreover, sleep deprivation can impair our ability to make informed and healthy food choices, leading to a higher likelihood of consuming unhealthy and calorie-dense snacks and meals.
3. Circadian Rhythm Disruption and Metabolic Health
The disruption of our natural circadian rhythm, often caused by irregular sleep patterns and shift work, can have detrimental effects on our metabolic health. Poor sleep habits can disturb the body's metabolic processes, interfering with glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity. As a result, individuals with disrupted circadian rhythms are more susceptible to weight gain and an increased risk of developing conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
4. Sleep Deprivation and Muscle Mass
Sleep deprivation not only affects our appetite and food choices but also has implications for muscle mass maintenance. During sleep, our bodies undergo important repair and recovery processes, including muscle protein synthesis. Insufficient sleep duration and poor sleep quality can disrupt these processes, impairing muscle recovery and growth. This can lead to decreased muscle mass and a higher proportion of body fat, affecting overall body composition.
Conclusion:
It is clear that sleep and weight management are intricately connected, with surprising interactions that go beyond conventional wisdom. Prioritizing adequate and quality sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being.
The Connection Between Sleep and Cardiovascular Health
Sleep plays a crucial role in promoting overall well-being by impacting both mental and physical health. While the relationship between sleep and mental and physical well-being is well-established, an often overlooked aspect is the link between sleep and cardiovascular health.
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. Research has shown that inadequate sleep duration and poor quality sleep are associated with an increased risk of developing various cardiovascular conditions. These conditions include heart disease, hypertension, stroke, and obesity.
During sleep, the body undergoes important processes that support cardiovascular health. One such process is the regulation of blood pressure. Adequate sleep helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels, reducing the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
Additionally, sleep plays a crucial role in regulating the body's inflammatory processes. Chronic inflammation has been linked to the development of cardiovascular diseases, and quality sleep helps modulate the body's inflammatory response, reducing the risk of such conditions.
Furthermore, sleep deprivation can negatively impact the body's metabolism and lead to weight gain, increasing the risk of conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. These conditions are known risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.
In conclusion, recognizing the connection between sleep and cardiovascular health is of utmost importance in promoting overall well-being. Prioritizing quality sleep can help lower the risk of various cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, stroke, and obesity.
Strategies for Enhancing Sleep Quality and Quantity

In this section, we will explore various approaches to improve the overall quality and quantity of sleep. The importance of a good night's rest in fostering mental and physical well-being cannot be overstated. Therefore, implementing effective strategies to optimize sleep patterns is crucial.
1. Establish a Consistent Sleep Routine:
- Regularly go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a soothing pre-sleep routine to signal to your body that it is time to relax and prepare for rest.
- Avoid engaging in stimulating activities, such as using electronic devices or engaging in mentally-demanding tasks, close to bedtime.
2. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment:
- Ensure your sleep environment is dark, quiet, and cool.
- Invest in a comfortable mattress, pillows, and bedding that promote relaxation and proper spinal alignment.
- Minimize external disruptions by using earplugs, an eye mask, or white noise machines if necessary.
3. Adopt Healthy Lifestyle Habits:
- Avoid consuming stimulants, such as caffeine and nicotine, close to bedtime.
- Engage in regular exercise during the day to promote better sleep quality.
- Maintain a balanced diet, avoiding heavy meals and excessive fluid intake before bedtime.
4. Manage Stress Levels:
- Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in relaxing activities before bed.
- Consider keeping a journal to express and release any thoughts or worries that may interfere with sleep.
- Seek support from professionals, such as therapists or counselors, if stress or anxiety persistently disrupts sleep.
5. Limit Exposure to Artificial Light:
- Avoid using electronic devices with screens, such as smartphones and laptops, in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Dim the lights in your home and consider using blue-light filters on electronic devices to minimize disruption to your natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Expose yourself to natural light during the day to help regulate your circadian rhythm.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a conducive sleep environment and establish healthy sleep habits that contribute to both mental and physical well-being.
FAQ
Why is sleep important for mental and physical well-being?
Sleep is important for mental and physical well-being because it allows the body to repair and rejuvenate itself. During sleep, the brain consolidates memories and processes emotions, promoting mental clarity and emotional stability. Additionally, sleep plays a vital role in promoting physical health by boosting the immune system, supporting growth and development, and preventing chronic illnesses such as heart disease and diabetes.
How much sleep is necessary for optimal mental and physical health?
The amount of sleep needed for optimal mental and physical health varies depending on age and individual differences. However, generally, adults require around 7-9 hours of sleep per night, while teenagers need 8-10 hours, and younger children and infants typically need more. It's important to prioritize and schedule enough sleep to ensure proper functioning of both the mind and body.
What are the consequences of sleep deprivation on mental and physical well-being?
Sleep deprivation can have severe consequences on mental and physical well-being. In terms of mental health, lack of sleep can result in impaired cognitive function, memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and increased risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. On the physical side, sleep deprivation can weaken the immune system, increase the risk of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes, impair motor skills, and lead to chronic fatigue and low energy levels.
Are there any strategies to improve sleep quality?
Yes, there are several strategies to improve sleep quality. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, practicing a relaxing bedtime routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding stimulating activities and electronic devices before bed, limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, and engaging in regular exercise can all contribute to better sleep quality. It is important to find what works best for you and implement healthy sleep habits into your daily routine.
What are some tips for dealing with insomnia and achieving restful sleep?
If you struggle with insomnia or have difficulty achieving restful sleep, there are several tips that may help. It is beneficial to establish a consistent sleep-wake schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine. Avoiding stimulating activities and electronic devices close to bedtime, keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet, managing stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, and avoiding napping during the day can also aid in overcoming insomnia and achieving restful sleep.
How does sleep affect our mental well-being?
Sleep plays a crucial role in promoting our mental well-being. During sleep, our brain processes emotions and consolidates memories, which helps regulate our mood and emotional responses. Lack of sleep can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and mood disorders.
Can lack of sleep impact our physical health?
Yes, lack of sleep can significantly impact our physical health. Sleep deprivation has been linked to a higher risk of chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and weakened immune system. It also affects our body's ability to recover, repair tissues, and maintain a healthy metabolism.



